A marine biologist focuses on studying creatures that are marine or saltwater in nature. Numerous marine scientists work with marine animals such as fish and whales, while others research marine plant life and microscopic organisms’ behaviors and ecosystems.
A marine biologist’s job varies not only in the types of species being studied but also in the manner in which research is done. Many work in the field of observation and conservation, while others work in research labs, and many work in both environments.
Marine biologists’ work can concentrate on marine ecology, conservation, and the understanding of marine organisms’ evolution, behavior, and physiology.
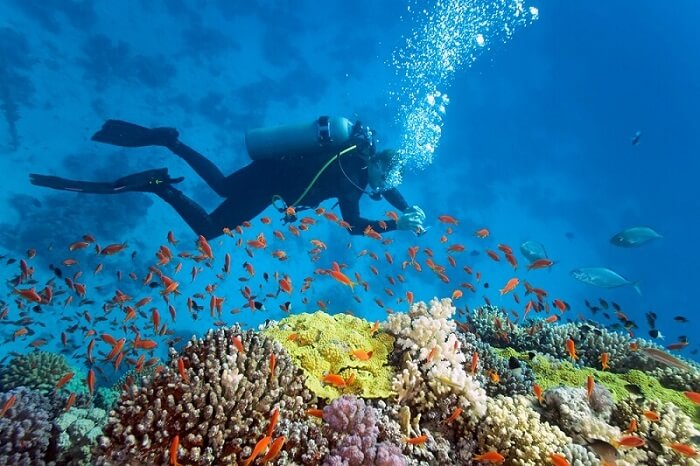

Training to Become a Marine Biologist
Marine biologists, like all researchers, seek a rigorous education that involves studying at the undergraduate and graduate levels. Some prospective marine biologists study biology or zoology as undergraduates and some select marine biology majors. Nevertheless, earning a degree in marine biology is not a requirement for becoming a marine biologist. In addition to pursuing a natural science education, it may be useful to develop a strong background in engineering, mathematics, or computer science.
In addition to taking classes in physics, chemistry, calculus, and math, students in biology programs study biochemistry, cell biology, ecology, and evolution. Students in biology can choose elective courses to complement their major routes, and some schools offer courses in marine ecology and zoology, which is the study of the kingdom of animals.
Biology programs have a significant component of the laboratory, so students gain experience working with laboratory instruments and observing procedures for laboratory and study.
Several colleges and universities offer marine biology undergraduate programs. Students take courses focusing on oceanography, marine ecosystems, aquatic invertebrates, marine vertebrates, and marine ecology. Students may also have opportunities to do important fieldwork under the supervision of marine biologists conducting research by completing a program near an ocean.
Average Salary as a Marine Biologist
According to CareerExplorer, in the US, a marine biologist can expect to make an average yearly salary of $32,159. Wages typically start at around $24,166 and go up to $71,561.
Where to Apply for a Job as a Marine Biologist
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, between 2012 and 2020, jobs for zoologists and wildlife biologists will rise by 5%, which is faster than the average growth for all occupations.
Although this career requires studying the effects of human activity on marine life and establishing conservation strategies to preserve marine life, recruiting marine biologists is often dependent on budgets from the state and federal governments.
Many people in this profession work for government agencies in state and federal government. Generally, these positions provide more job security and more room for growth. Most work in private laboratories for research or consulting firms. Others work or become faculty members in universities with aquariums, zoos, or museums. Some become teachers of high school science, too.
Job Description as a Marine Biologist
- Review studies and literature on recent findings in the field.
- Collecting field data and tracking specimens of biological samples and non-living media to conduct analyses.
- Conduct studies on behavior and relationships between organisms in the marine environment.
- Analyze the evolution and distribution of plants and their habitat in the ocean and preserve the instrumentation used to track oceans.
Conclusion
Marine biology is a vast field in which a wide variety of species are studied. There are many academic societies dedicated to bringing together scientists studying specific animals, plants, and microorganisms. For more science-related careers, click here.